




在早前的一项研究中,糖尿病持续时间短的患者能通过早期联合治疗(维格列汀和二甲双胍)使血糖水平正常化 [54] 。因此,建议降低目标HbA1c水平是必要的,并应当强调其对于糖尿病缓解的重要性。如前所述,代谢手术是一种很好的治疗选择,但它的局限性在于接受治疗的患者必须在限制性体重或BMI范围内(体重指数BMI≥40.0kg/m 2 ;亚洲人BMI≥37.5kg/m 2 )。此外,单纯的强化生活方式改变会使患者难以保持体重和糖尿病缓解。因此,通过改变生活方式联合药物治疗达到血糖正常,可以促进糖尿病的持续缓解。血糖正常后,如果在保持体重的同时对药物减量,则可持续缓解。然而,糖尿病缓解的药物治疗策略有两个基本前提。一是低血糖风险低:如果低血糖频繁发生,则不能通过足量使用疗效高的药物来达到血糖正常。二是药物疗法需要对减肥有益。通常,钠-葡萄糖共转运蛋白2抑制剂(SGLT2i)和GLP-1受体激动剂(GLP-1 RA)都会导致体重减轻。然而,SGLT2i的减肥效果低于GLP-1 RA。同时满足以上两点的药物类型是GLP-1 RA,特别是利拉鲁肽和司美格鲁肽,这两者最初用于治疗2型糖尿病,可有效降低血糖并减轻体重。由于GLP-1对食欲和能量平衡的调节作用,GLP-1 RA是治疗肥胖症的药物。GLP-1从L细胞中释放,并能够刺激2型糖尿病患者的胰岛素分泌。GLP-1的另一个重要作用是延迟胃排空。此外,在中枢神经系统中GLP-1受体位于下丘脑,这是调节食物摄入的部分。因此,GLP-1 RA能通过多种机制减轻体重 [55] (如图3-6所示)。同时,《ADA/EASD共识》中指出GLP-1 RA因其高效性和安全性而优于胰岛素 [56] 。
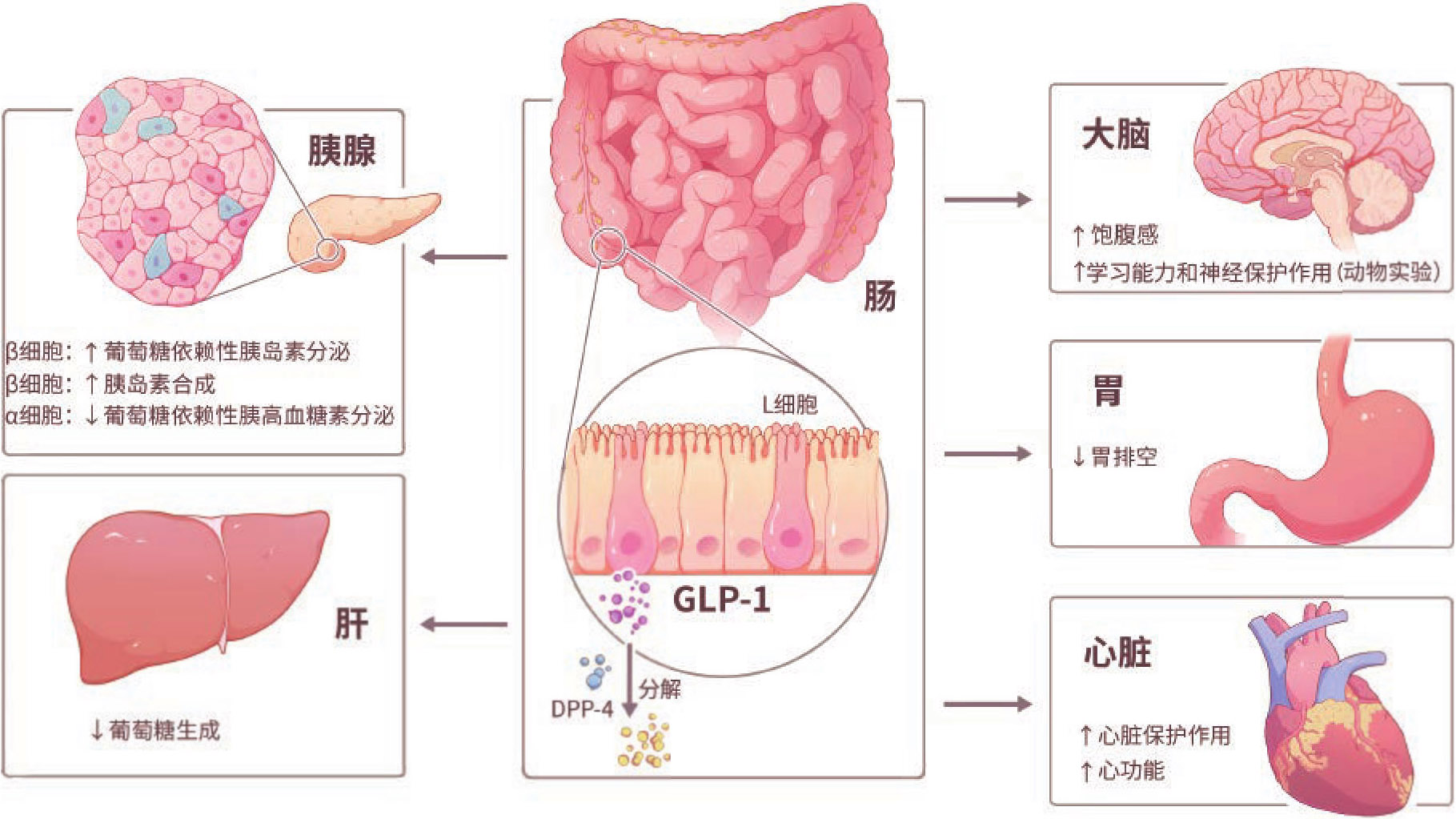
图3-6 GLP-1的作用机制与2型糖尿病缓解
利拉鲁肽和司美格鲁肽被批准为抗糖尿病药物,前者每天皮下给药一次,后者每周皮下给药一次。而更高剂量的这两种药物被开发用于2型糖尿病患者或非2型糖尿病的肥胖患者治疗肥胖以及控制血糖。早在2014年,美国食品和药物管理局(FDA)批准了利拉鲁肽用于成人肥胖症的治疗。2022年12月4日美国FDA批准了利拉鲁肽注射液的说明书标签更新,准许其用于治疗体重在60kg以上、身体质量指数(BMI)在30kg/m 2 或以上的12~17岁青少年肥胖症,作为低热量饮食和增加运动的辅助疗法。在非糖尿病和糖尿病患者肥胖和糖尿病前期试验(SCALE)中,与安慰剂相比,3.0mg利拉鲁肽减轻了体重(差异为-5.6kg;95%可信区间为-6.0~-5.1kg;P<0.001)。此外,在3年的随访中,利拉鲁肽组2型糖尿病延缓发生,其发生时间是安慰剂组的2.7倍(95%CI,1.9~3.9;P<0.0001),相应的风险比(HR)为0.21(95%CI,0.13~0.34) [9] 。2021年6月美国FDA批准使用2.4mg的司美格鲁肽,用于肥胖或超重的、伴随至少一种体重相关疾病(如高血压、2型糖尿病或高胆固醇)的成年患者减肥。其在国内截至2023年2月尚没有获批治疗肥胖症。在司美格鲁肽治疗肥胖患者的效果(STEP)2期试验中,从基线到第68周,患者平均体重的估计变化为-9.6%(标准误差,0.4)。给予2.4mg司美格鲁肽的患者的HbA1c浓度从基线到第68周降低了1.6%(标准误差,0.1)。给予2.4mg司美格鲁肽的患者第68周基线体重减少≥10%的比例为45.6%,给予2.4mg的司美格鲁肽并达到HbA1c≤6.5%水平的患者比例为67.5%。结果表明,其降糖效果和减肥效果与代谢手术一样有意义 [57] 。
最近,一种GLP-1/GIP双受体激动剂替尔泊肽在肥胖糖尿病患者的治疗中显示出令人鼓舞的结果 [58] 。在健康个体中,与单独使用每种激素相比,GIP和GLP-1 RA的联合使用在增加胰岛素应答方面具有相加效应。然而,在2型糖尿病患者中,短时间内联合使用GIP和GLP-1 RA不会产生比单独使用GLP-1 RA更强的促胰岛素分泌作用。替尔泊肽作为一种GLP-1/GIP双受体激动剂,是根据天然GIP序列配制的含有39个氨基酸的合成线性肽。它与天然GIP具有相似的GIP受体亲和力,对GLP-1受体亲和力是天然GLP-1的1/6。在SURPASS-1中,替尔泊肽显著改善了血糖和体重。替尔泊肽15mg组患者HbA1c降低2.07%,体重平均减轻9.5kg。HbA1c水平达到≤6.5%的患者比例为86% [58] 。体重减少≥10%的患者比例达47%。此外,替尔泊肽通过了全球Ⅲ期临床研究(SURPASS-2),是第一个完成Ⅲ期临床试验的GLP-1/GIP双受体激动剂。在SURPASS-2试验中,将替尔泊肽与司美格鲁肽1mg进行比较,替尔泊肽优于司美格鲁肽。另一方面,两项试验均未报告临床显著低血糖(血糖<3.0mmol/L)。这些特征可以满足糖尿病缓解的所有要求 [59] 。除了尚未在临床上联合替尔泊肽,肠促胰岛素已通过联合代谢手术和强化生活方式的改变来维持体重减轻和糖尿病缓解 [60] 。在2型糖尿病病程相对较短的情况下,GLP-1 RA单独使用导致的体重减轻可能足以实现糖尿病缓解。即使在停止肠促胰岛素刺激后,显著的体重减轻和血糖正常化也有助于维持糖尿病的缓解 [61] 。
①Lean ME,Leslie WS,et al.Primary careled weight management for remission of type 2 diabetes (DiRECT):an open-label,clusterrandomised trial[J].Lancet,2018,391:541-551.
②Captieux M,Fleetwood K,Kennon B,Sattar N,Lindsay R,Guthrie B,Wild SH.Scottish Diabetes Research Network Epidemiology G:Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes remission in Scotland in 2019:A cross-sectional populationbased study[J].PLoS Med,2021,18:e1003828.
③Riddle MC,Cefalu WT,Evans PH,Gerstein HC,Nauck MA,Oh WK,Rothberg AE,le Roux CW,Rubino F,Schauer P,Taylor R,Twenefour D.Consensus Report:Definition and Interpretation of Remission in Type 2 Diabetes[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2022,107:1-9.
④Marselli L,Piron A,Suleiman M,Colli ML,Yi X,Khamis A,Carrat GR,Rutter GA,Bugliani M,Giusti L,Ronci M,Ibberson M,Turatsinze JV,Boggi U,De Simone P,De Tata V,Lopes M,Nasteska D,De Luca C,Tesi M,Bosi E,Singh P,Campani D,Schulte AM,Solimena M,Hecht P,Rady B,Bakaj I,Pocai A,Norquay L,Thorens B,Canouil M,Froguel P,Eizirik DL,Cnop M,Marchetti P.Persistent or Transient Human beta Cell Dysfunction Induced by Metabolic Stress:Specifi c Signatures and Shared Gene Expression with Type 2 Diabetes[J].Cell Rep,2020,33:108466.
⑤Paolisso G,Gambardella A,Amato L,Tortoriello R,D’Amore A,Varricchio M,D’Onofrio F.Opposite effects of short- and long-term fatty acid infusion on insulin secretion in healthy subjects[J].Diabetologia,1995,38:1295-1299.
⑥Cusi K,Kashyap S,Gastaldelli A,Bajaj M,Cersosimo E.Effects on insulin secretion and insulin action of a 48-h reduction of plasma free fatty acids with acipimox in nondiabetic subjects genetically predisposed to type 2 diabetes[J].Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab,2007,292:1775-1781.
⑦Al-Mrabeh A,Zhyzhneuskaya SV,Peters C,Barnes AC,Melhem S,Jesuthasan A,Aribisala B,Hollingsworth KG,Lietz G,Mathers JC,Sattar N,Lean MEJ,Taylor R.Hepatic Lipoprotein Export and Remission of Human Type 2 Diabetes after Weight Loss[J].Cell Metab,2020,31:233-249.
⑧Marrano N,Biondi G,Cignarelli A,Perrini S,Laviola L,Giorgino F,Natalicchio A.Functional loss of pancreatic islets in type 2 diabetes:How can we halt it?[J].Metabolism,2020,110:154304.
⑨le Roux CW,Astrup A,Fujioka K,Greenway F,Lau DCW,Van Gaal L,Ortiz RV,Wilding JPH,Skjoth TV,Manning LS,Pi-Sunyer X,Group SOPN-S.3 years of liraglutide versus placebo for type 2 diabetes risk reduction and weight management in individuals with prediabetes:a randomised,double-blind trial[J].Lancet,2017,389:1399-1409.
⑩Raverdy V,Cohen RV,Caiazzo R,Verkindt H,Petry TBZ,Marciniak C,Legendre B,Bauvin P,Chatelain E,Duhamel A,Drumez E,Oukhouya-Daoud N,Chetboun M,Baud G,Ahlqvist E,Wierup N,Asplund O,Laferrere B,Groop L,Pattou F.Data-driven subgroups of type 2 diabetes,metabolic response,and renal risk profile after bariatric surgery:a retrospective cohort study[J].Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol,2022,10:167-176.
⑪Fellici AC,Lambert G,Lima MM,Pareja JC,Rodovalho S,Chaim EA,Geloneze B.Surgical treatment of type 2 diabetes in subjects with mild obesity:mechanisms underlying metabolic improvements[J].Obes Surg,2015,25:36-44.
⑫Marshak S,Leibowitz G,Bertuzzi F,Socci C,Kaiser N,Gross DJ,Cerasi E,Melloul D.Impaired beta-cell functions induced by chronic exposure of cultured human pancreatic islets to high glucose[J].Diabetes,1999,48:1230-1236.
⑬Maris M,Waelkens E,Cnop M,D’Hertog W,Cunha DA,Korf H,Koike T,Overbergh L,Mathieu C.Oleate-induced beta cell dysfunction and apoptosis:a proteomic approach to glucolipotoxicity by an unsaturated fatty acid[J].J Proteome Res,2011,10:3372-3385.
⑭Marchetti P,Del Guerra S,Marselli L,Lupi R,Masini M,Pollera M,Bugliani M,Boggi U,Vistoli F,Mosca F,Del Prato S.Pancreatic islets from type 2 diabetic patients have functional defects and increased apoptosis that are ameliorated by metformin[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2004,89:5535-5541.
⑮Lupi R,Mancarella R,Del Guerra S,Bugliani M,Del Prato S,Boggi U,Mosca F,Filipponi F,Marchetti P.Effects of exendin-4 on islets from type 2 diabetes patients[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2008,10:515-519.
⑯Cunha DA,Ladriere L,Ortis F,Igoillo-Esteve M,Gurzov EN,Lupi R,Marchetti P,Eizirik DL,Cnop M.Glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists protect pancreatic beta-cells from lipotoxic endoplasmic reticulum stress through upregulation of BiP and JunB[J].Diabetes,2009,58:2851-2862.
⑰Pearson GL,Gingerich MA,Walker EM,Biden TJ,Soleimanpour SA.A Selective Look at Autophagy in Pancreatic Beta-cells[J].Diabetes,2021,70:1229-1241.
⑱Taylor R.Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes:tracing the reverse route from cure to cause[J].Diabetologia,2008,51:1781-1789.
⑲Taylor R,Al-Mrabeh A,Zhyzhneuskaya S,Peters C,Barnes AC,Aribisala BS,Hollingsworth KG,Mathers JC,Sattar N,Lean MEJ.Remission of Human Type 2 Diabetes Requires Decrease in Liver and Pancreas Fat Content but Is Dependent upon Capacity for beta Cell Recovery[J].Cell Metab,2018,28:667.
⑳Tilg H,Moschen AR,Roden M.NAFLD and diabetes mellitus[J].Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol,2017,14:32-42.
㉑Sofat R,Cooper JA,Kumari M,Casas JP,Mitchell JP,Acharya J,Thom S,Hughes AD,Humphries SE,Hingorani AD.Circulating Apolipoprotein E Concentration and Cardiovascular Disease Risk:Meta-analysis of Results from Three Studies[J].PLoS Med,2016,13:e1002146.
㉒Kawano Y,Cohen DE.Mechanisms of hepatic triglyceride accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J].J Gastroenterol,2013,48:434-441.
㉓Schrauwen P,van Marken Lichtenbelt WD,Spiegelman BM.The future of brown adipose tissues in the treatment of type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetologia,2015,58:1704-1707.
㉔Brereton MF,Iberl M,Shimomura K,Zhang Q,Adriaenssens AE,Proks P,Spiliotis II,Dace W,Mattis KK,Ramracheya R,Gribble FM,Reimann F,Clark A,Rorsman P,Ashcroft FM.Reversible changes in pancreatic islet structure and function produced by elevated blood glucose[J].Nat Commun,2014,5:4639.
㉕Patel S,Alvarez-Guaita A,Melvin A,Rimmington D,Dattilo A,Miedzybrodzka EL,Cimino I,Maurin AC,Roberts GP,Meek CL,Virtue S,Sparks LM,Parsons SA,Redman LM,Bray GA,Liou AP,Woods RM,Parry SA,Jeppesen PB,Kolnes AJ,Harding HP,Ron D,Vidal-Puig A,Reimann F,Gribble FM,Hulston CJ,Farooqi IS,Fafournoux P,Smith SR,Jensen J,Breen D,Wu Z,Zhang BB,Coll AP,Savage DB,O’Rahilly S.GDF15 Provides an Endocrine Signal of Nutritional Stress in Mice and Humans[J].Cell Metab,2019,29:707-718,e708.
㉖Jang C,Oh SF,Wada S,Rowe GC,Liu L,Chan MC,Rhee J,Hoshino A,Kim B,Ibrahim A,Baca LG,Kim E,Ghosh CC,Parikh SM,Jiang A,Chu Q,Forman DE,Lecker SH,Krishnaiah S,Rabinowitz JD,Weljie AM,Baur JA,Kasper DL,Arany Z.A branched-chain amino acid metabolite drives vascular fatty acid transport and causes insulin resistance[J].Nat Med,2016,22:421-426.
㉗Taylor R,Al-Mrabeh A,Sattar N.Understanding the mechanisms of reversal of type 2 diabetes[J].Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol,2019,7:726-736.
㉘Al-Mrabeh A,Hollingsworth KG,Steven S,Taylor R.Morphology of the pancreas in type 2 diabetes:effect of weight loss with or without normalisation of insulin secretory capacity[J].Diabetologia,2016,59:1753-1759.
㉙Drucker DJ.The biology of incretin hormones[J].Cell Metab,2006,3:153-165.
㉚Weiss R.Effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on beta-cell function[J].Diabetes,2014,63:1171-1173.
㉛Borgeraas H,Hjelmesaeth J,Birkeland KI,Fatima F,Grimnes JO,Gulseth HL,Halvorsen E,Hertel JK,Hillestad TOW,Johnson LK,Karlsen TI,Kolotkin RL,Kvan NP,Lindberg M,Lorentzen J,Nordstrand N,Sandbu R,Seeberg KA,Seip B,Svanevik M,Valderhaug TG,Hofso D.Single-centre,triple-blinded,randomised,1-year,parallel-group,superiority study to compare the effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy on remission of type 2 diabetes and beta-cell function in subjects with morbid obesity:a protocol for the Obesity surgery in Tonsberg (Oseberg) study[J].BMJ Open,2019,9:e024573.
㉜Buser A,Joray C,Schiavon M,Kosinski C,Minder B,Nakas CT,Man CD,Muka T,Herzig D,Bally L.Effects of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy on beta-Cell Function at 1 Year After Surgery:A Systematic Review[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2022,107:3182-3197.
㉝Wilson J,Docherty P,Stubbs R,Chase JG,Krebs J.Assessment of the Dynamic Insulin Secretion and Sensitivity Test (DISST) Pre and Post Gastric bypass Surgery[J].Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes,2020,128:164-169.
㉞Bradley D,Magkos F,Klein S.Effects of bariatric surgery on glucose homeostasis and type 2 diabetes[J].Gastroenterology,2012,143:897-912.
㉟Hindso M,Hedback N,Svane MS,Moller A,Martinussen C,Jorgensen NB,Dirksen C,Gasbjerg LS,Kristiansen VB,Hartmann B,Rosenkilde MM,Holst JJ,Madsbad S,Bojsen-Moller KN.The importance of endogenously secreted GLP-1 and GIP for postprandial glucose tolerance and beta-cell function after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy surgery[J].Diabetes,2023,72(3):336-347.
㊱Romero F,Nicolau J,Flores L,Casamitjana R,Ibarzabal A,Lacy A,Vidal J.Comparable early changes in gastrointestinal hormones after sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-En-Y gastric bypass surgery for morbidly obese type 2 diabetic subjects[J].Surg Endosc,2012,26:2231-2239.
㊲Yang C,Brecht J,Weiss C,Reissfelder C,Otto M,Buchwald JN,Vassilev G.Serum Glucagon,Bile Acids,and FGF-19:Metabolic Behavior Patterns After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy[J].Obes Surg,2021,31:4939-4946.
㊳Kohli R,Bradley D,Setchell KD,Eagon JC,Abumrad N,Klein S.Weight loss induced by Roux-en-Y gastric bypass but not laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding increases circulating bile acids[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013,98:e708-712.
㊴Munzker J,Haase N,Till A,Sucher R,Haange SB,Nemetschke L,Gnad T,Jager E,Chen J,Riede SJ,Chakaroun R,Massier L,Kovacs P,Ost M,Rolle-Kampczyk U,Jehmlich N,Weiner J,Heiker JT,Kloting N,Seeger G,Morawski M,Keitel V,Pfeifer A,von Bergen M,Heeren J,Krugel U,Fenske WK.Functional changes of the gastric bypass microbiota reactivate thermogenic adipose tissue and systemic glucose control via intestinal FXR-TGR5 crosstalk in diet-induced obesity[J].Microbiome,2022,10:96.
㊵Wagner NRF,Zaparolli MR,Cruz MRR,Schieferdecker MEM,Campos ACL.Postoperative Changes in Intestinal Microbiota and Use of Probiotics in Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Vertical Gastrectomy:An Integrative Review[J].Arq Bras Cir Dig,2018,31:e1400.
㊶Baud G,Daoudi M,Hubert T,Raverdy V,Pigeyre M,Hervieux E,Devienne M,Ghunaim M,Bonner C,Quenon A,Pigny P,Klein A,Kerr-Conte J,Gmyr V,Caiazzo R,Pattou F.Bile Diversion in Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Modulates Sodium-Dependent Glucose Intestinal Uptake[J].Cell Metab,2016,23:547-553.
㊷Rosenstock J,Cefalu WT,Lapuerta P,Zambrowicz B,Ogbaa I,Banks P,Sands A.Greater dose-ranging effects on A1C levels than on glucosuria with LX4211,a dual inhibitor of SGLT1 and SGLT2,in patients with type 2 diabetes on metformin monotherapy[J].Diabetes Care,2015,38:431-438.
㊸Du J,Hu C,Bai J,Peng M,Wang Q,Zhao N,Wang Y,Wang G,Tao K,Wang G,Xia Z.Intestinal Glucose Absorption Was Reduced by Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy via Decreased Gastric Leptin Secretion[J].Obes Surg,2018,28:3851-3861.
㊹Makinen J,Hannukainen JC,Karmi A,Immonen HM,Soinio M,Nelimarkka L,Savisto N,Helmio M,Ovaska J,Salminen P,Iozzo P,Nuutila P.Obesity-associated intestinal insulin resistance is ameliorated after bariatric surgery[J].Diabetologia,2015,58:1055-1062.
㊺Cavin JB,Couvelard A,Lebtahi R,Ducroc R,Arapis K,Voitellier E,Cluzeaud F,Gillard L,Hourseau M,Mikail N,Ribeiro-Parenti L,Kapel N,Marmuse JP,Bado A,Le Gall M.Differences in Alimentary Glucose Absorption and Intestinal Disposal of Blood Glucose After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass vs Sleeve Gastrectomy[J].Gastroenterology,2016,150:454-464,e459.
㊻Saeidi N,Meoli L,Nestoridi E,Gupta NK,Kvas S,Kucharczyk J,Bonab AA,Fischman AJ,Yarmush ML,Stylopoulos N.Reprogramming of intestinal glucose metabolism and glycemic control in rats after gastric bypass[J].Science,2013,341:406-410.
㊼Troy S,Soty M,Ribeiro L,Laval L,Migrenne S,Fioramonti X,Pillot B,Fauveau V,Aubert R,Viollet B,Foretz M,Leclerc J,Duchampt A,Zitoun C,Thorens B,Magnan C,Mithieux G,Andreelli F.Intestinal gluconeogenesis is a key factor for early metabolic changes after gastric bypass but not after gastric lap-band in mice[J].Cell Metab,2008,8:201-211.
㊽Camastra S,Vitali A,Anselmino M,Gastaldelli A,Bellini R,Berta R,Severi I,Baldi S,Astiarraga B,Barbatelli G,Cinti S,Ferrannini E.Muscle and adipose tissue morphology,insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function in diabetic and nondiabetic obese patients:effects of bariatric surgery[J].Sci Rep,2017,7:9007.
㊾Frikke-Schmidt H,O’Rourke RW,Lumeng CN,Sandoval DA,Seeley RJ.Does bariatric surgery improve adipose tissue function?[J].Obes Rev,2016,17:795-809.
㊿Xu XJ,Apovian C,Hess D,Carmine B,Saha A,Ruderman N.Improved Insulin Sensitivity 3 Months After RYGB Surgery Is Associated With Increased Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue AMPK Activity and Decreased Oxidative Stress[J].Diabetes,2015,64:3155-3159.
(51)Newsholme P,Cruzat V,Arfuso F,Keane K.Nutrient regulation of insulin secretion and action[J].J Endocrinol,2014,221:R105-120.
(52)Skytte MJ,Samkani A,Astrup A,Frystyk J,Rehfeld JF,Holst JJ,Madsbad S,Burling K,Fenger M,Thomsen MN,Larsen TM,Krarup T,Haugaard SB.Effects of carbohydrate restriction on postprandial glucose metabolism,beta-cell function,gut hormone secretion,and satiety in patients with Type 2 diabetes[J].Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab,2021,320:E7-18.
(53)Boden G,Sargrad K,Homko C,Mozzoli M,Stein TP.Effect of a low-carbohydrate diet on appetite,blood glucose levels,and insulin resistance in obese patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Ann Intern Med,2005,142:403-411.
(54)Matthews DR,Paldanius PM,Proot P,Chiang Y,Stumvoll M,Del Prato S,group Vs.Glycaemic durability of an early combination therapy with vildagliptin and metformin versus sequential metformin monotherapy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (VERIFY):a 5-year,multicentre,randomised,double-blind trial[J].Lancet,2019,394:1519-1529.
(55)Farr OM,Sofopoulos M,Tsoukas MA,Dincer F,Thakkar B,Sahin-Efe A,Filippaios A,Bowers J,Srnka A,Gavrieli A,Ko BJ,Liakou C,Kanyuch N,Tseleni-Balafouta S,Mantzoros CS.GLP-1 receptors exist in the parietal cortex,hypothalamus and medulla of human brains and the GLP-1 analogue liraglutide alters brain activity related to highly desirable food cues in individuals with diabetes:a crossover,randomised,placebo-controlled trial[J].Diabetologia,2016,59:954-965.
(56)American Diabetes A:9.Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment:Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021[J].Diabetes Care,2021,44:S111-S124.
(57)Davies M,Faerch L,Jeppesen OK,Pakseresht A,Pedersen SD,Perreault L,Rosenstock J,Shimomura I,Viljoen A,Wadden TA,Lingvay I,Group SS.Semaglutide 2.4mg once a week in adults with overweight or obesity,and type 2 diabetes (STEP 2):a randomised,double-blind,double-dummy,placebo-controlled,phase 3 trial[J].Lancet,2021,397:971-984.
(58)Rosenstock J,Wysham C,Frias JP,Kaneko S,Lee CJ,Fernandez Lando L,Mao H,Cui X,Karanikas CA,Thieu VT.Efficacy and safety of a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide in patients with type 2 diabetes(SURPASS-1):a double-blind,randomised,phase 3 trial[J].Lancet,2021,398:143-155.
(59)Frias JP,Davies MJ,Rosenstock J,Perez Manghi FC,Fernandez Lando L,Bergman BK,Liu B,Cui X,Brown K,Investigators S.Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide Once Weekly in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes[J].The New England journal of medicine,2021,385:503-515.
(60)Lundgren JR,Janus C,Jensen SBK,Juhl CR,Olsen LM,Christensen RM,Svane MS,Bandholm T,Bojsen-Moller KN,Blond MB,Jensen JB,Stallknecht BM,Holst JJ,Madsbad S,Torekov SS.Healthy Weight Loss Maintenance with Exercise,Liraglutide,or Both Combined[J].The New England journal of medicine,2021,384:1719-1730.
(61)Riddle MC,Cefalu WT,Evans PH,Gerstein HC,Nauck MA,Oh WK,Rothberg AE,le Roux CW,Rubino F,Schauer P,Taylor R,Twenefour D.Consensus report:definition and interpretation of remission in type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetologia,2021,64:2359-2366.