





扫码可见本项目相关参考资料
A machine tool performs three major functions:
(1)it rigidly supports the workpiece or its holder and the cutting tool;
(2)it provides relative motion between the workpiece and the cutting tool;
(3)it provides a range of feeds and speeds.
Machines used to remove metal in the form of chips are classified as follows:
(1) Machines using basically the single-point cutting tools include:engine lathes,turret lathes,tracing and duplicating lathes,single-spindle automatic lathes,multi-spindle automatic lathes,shapers and planers,boring machines.
(2)Machines using multipoint cutting tools include:drilling machines,milling machines,broaching machines,sawing machines,gear-cutting machines.
(3)Machines using random-point cutting tools(abrasive)include:cylindrical grinders,centreless grinders,and surface grinders.
Special metal removal methods include:chemical milling,electrical discharge machining,ultrasonic machining.
The lathe removes material by rotating the workpiece against a cutter to produce external or internal cylindrical or conical surfaces.It is commonly used for the production of surfaces by facing,in which the work piece is rotated while the cutting tool is moved perpendicularly to the axis of rotation.
The engine lathe,shown in Figure 3 1,is the basic turning machine from which other turning machines have been developed.The driving motor is located in the base and drives the spindle through a combination of belts and gears.The spindle is a sturdy hollow shaft,mounted between heavy-duty bearings,with the forward end used for mounting a drive plate to impart positive motion to the workpiece.The drive plate may be fastened to the spindle by threads,by a cam lock mechanism or by a threaded collar and key.
The lathe bed is cast iron and provides accurately ground sliding surfaces(way) on which the carriage rides [1] .The lathe carriage is an H-shaped casting on which the cutting tool is mounted in a tool holder.The apron hangs from the front of the carriage and contains the driving gears that move the tool and carriage along or across the way to provide the desired tool motion.
A compound rest,located above the carriage,provides for rotation of the tool holder through any desired angle.A hand wheel and feed screw are provided on the compound rest for linear motions of the tool.The cross feed is provided with another hand wheel and feed screw for moving the compound rest perpendicular to the lathe way.A gear train in the apron provides power feed for the carriage both along and across the way.The feed box contains gears to impart motion to the carriage and control the rate at which the tool moves relative to the workpiece.Since the transmission in the feed box gearing is driven by the spindle gears,the feeds are directly related to spindle speed.The feed box gearing is also used in thread cutting and provides from 4 to 224 threads per in.
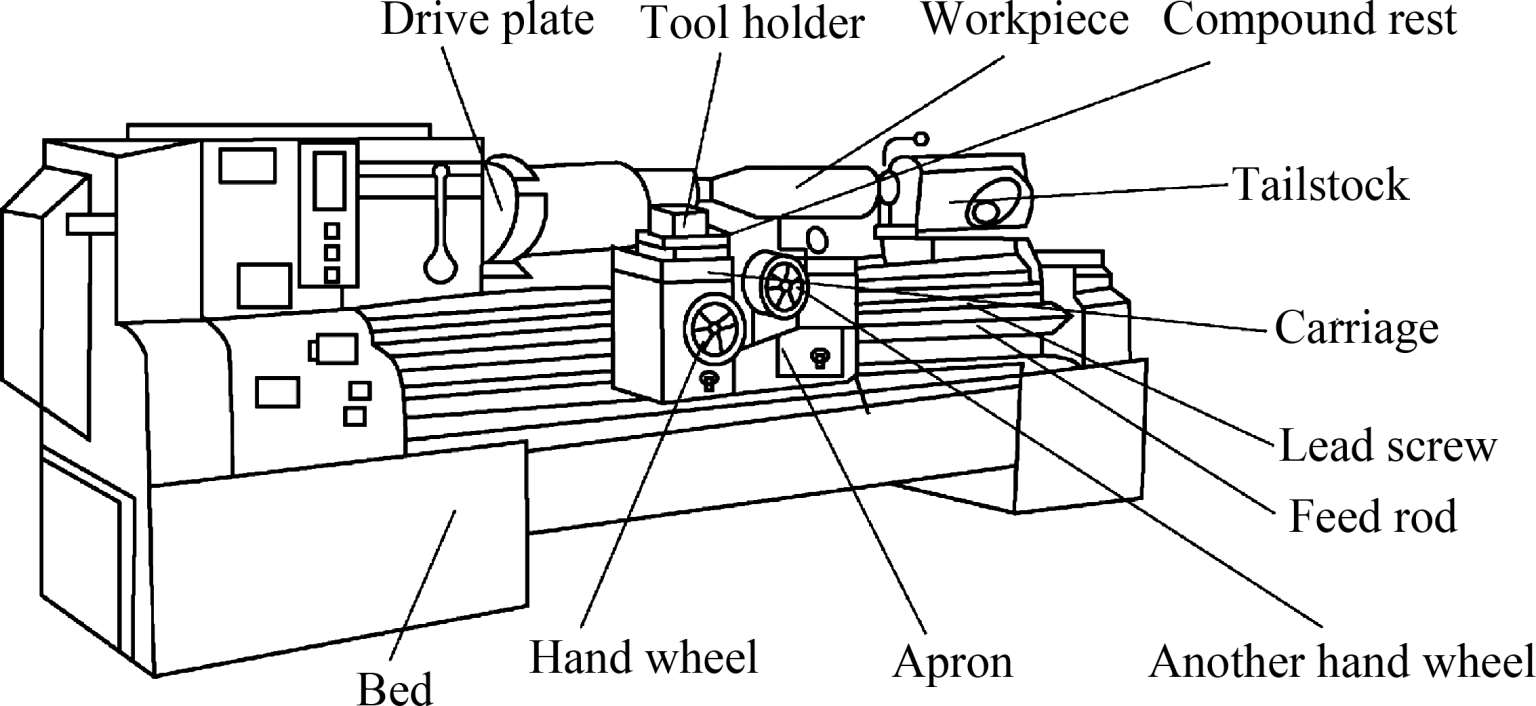
Figure3-1 Engine lathe
The turret lathe is basically an engine lathe with certain additional features to provide for semiautomatic operation and to reduce the opportunity for human error.The carriage of the turret lathe is provided with T-slots for mounting a tool-holding device on both sides of the lathe ways with tools properly set for cutting when rotated into position.The carriage is also equipped with automatic stops that control the tool travel and provide good reproduction of cuts.The tailstock of the turret lathe is of hexagonal design,in which six tools can be mounted.Although a large amount of time is consumed in setting up the tools and stops for operation,the turret lathe,once set,can continue to duplicate operations with a minimum of operator skill until the tools become dulled and need replacing.Thus,the turret lathe is economically feasible only for production work,where the amount of time necessary to prepare the machine for operation is justifiable in terms of the number of part to be made.
The multi-spindle automatic lathe is provided with four,five,six,or eight spindles,with one workpiece mounted in each spindle.The spindles index around a central shaft,with the main tool slide accessible to all spindles.Each spindle position is provided with a side tool-slide operated independently.Since all of the slides are operated by cams,the preparation of this machine may take several days,and a production run of at least 5 000 parts is needed to justify its use.The principal advantage of this machine is that all tools work simultaneously,and one operator can handle several machines.For relatively simple parts,multi-spindle automatic lathes can turn out finished products at the rate of 1 every 5 sec.
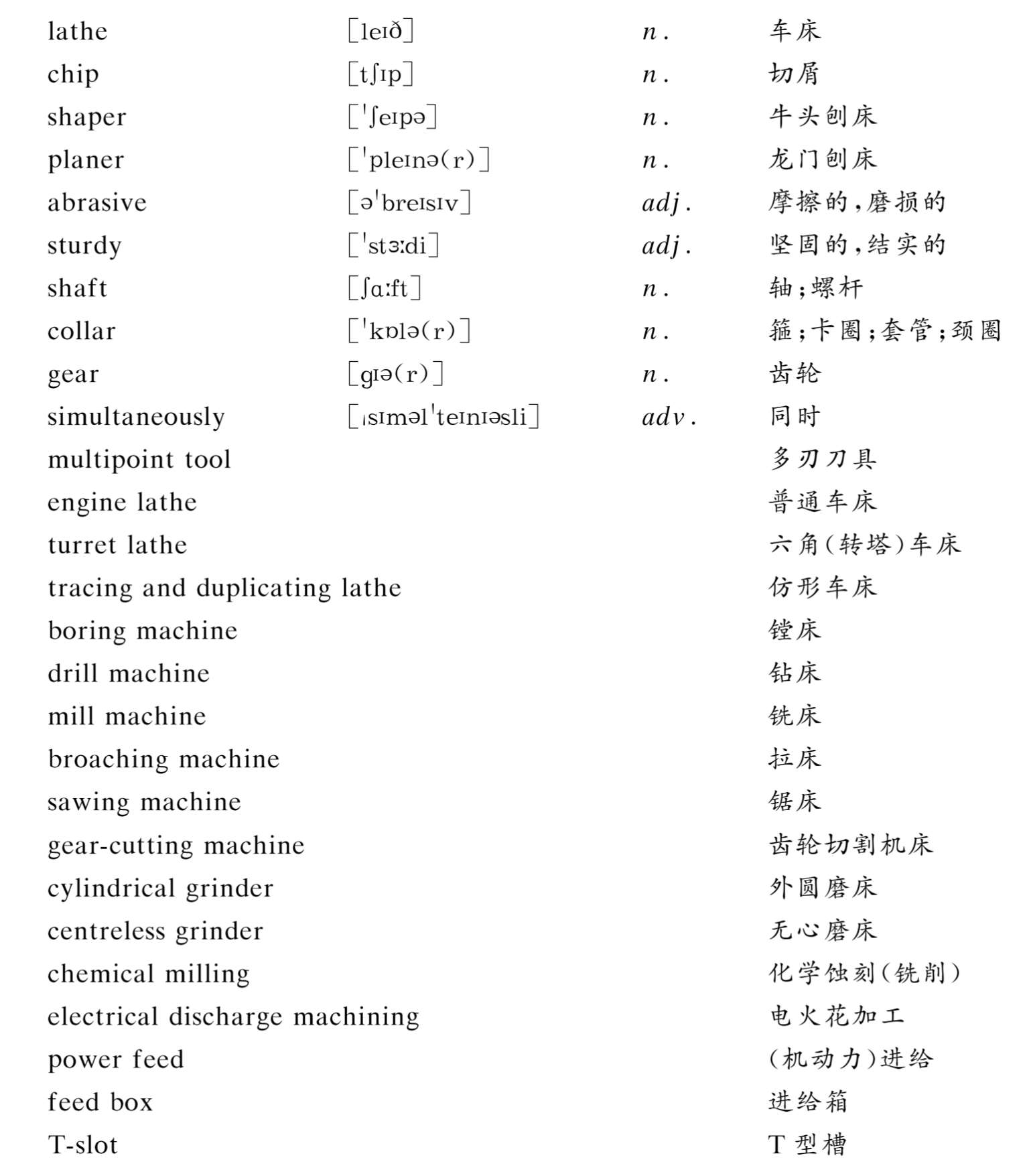
The lathe bed is cast iron and provides accurately ground sliding surfaces(way) on which the carriage rides.
车身是铸铁件,它提供精确磨削过的滑动表面(导轨),上面放有拖板。(ground是grind的过去分词,作定语用)
一台机床主要有以下三个功能:
(1)固定工件或者刀架和刀具;
(2)控制工件和刀具之间的相对运动;
(3)提供一定范围的走刀和切削速度。
以去除切屑形式来加工金属的机床分类如下:
(1)主要使用单点切削刀具的机床包括:普通车床、塔式车床、仿形车床、单轴自动车床、多轴自动车床、牛头刨床和龙门刨床、镗床。
(2)使用多点切削刀具的机床包括:钻床、铣床、拉床、锯床、齿轮切割机床。
(3)使用随机点切削刀具的机床包括:外圆磨床、无心磨床、平面磨床。
特殊金属切削方法包括:化学蚀刻铣削、电火花加工、超声波加工。
车床借助于转动的工件对着刀具来切去金属材料,以产生外圆柱面、内圆柱面或锥形表面。车床普遍靠端面切削来加工工件表面。在端面切削加工中,工件旋转,而刀具作垂直于回转轴线方向的移动。
普通车床,如图3-1所示,作为最基本的车床,是研制其他车床的基础。驱动电机装在床身底部并通过齿轮、皮带来驱动主轴。主轴是一根坚固的空心轴,装在重型轴承之间,其前端用来安装驱动盘(花盘),以便把确定的运动传到工件上。该驱动盘可借助螺纹、凸轮锁紧机构或借助一个螺纹垫圈和键固定在主轴上。
车床的床身是铸铁件,它提供精确磨削过的滑动表面(导轨),上面放有拖板。车床拖板是H型的铸件,刀具安装在拖板的刀架上。溜板箱装在拖板前面,内装有驱动齿轮,可以顺着导轨或横跨导轨移动刀具和拖板,以提供所希望的刀具运动。
拖板上面的小刀架能使刀的夹具旋转任意角度。小刀架上的手轮和丝杆可以使刀具作线性运动,另一个手轮和进给螺纹提供横向进给,使小刀架垂直于导轨移动。溜板箱中的齿轮可以在拖板沿着导轨和横跨导轨移动时提供动力进给。进给箱齿轮将运动传给拖板并控制刀具相对于工件的运动速度。由于进给箱的移动运动是由主轴齿轮驱动的,因此,进给量直接与主轴速度有关。进给箱齿轮传动机构也用于加工螺纹并能加工4扣~224扣/英寸的螺纹。
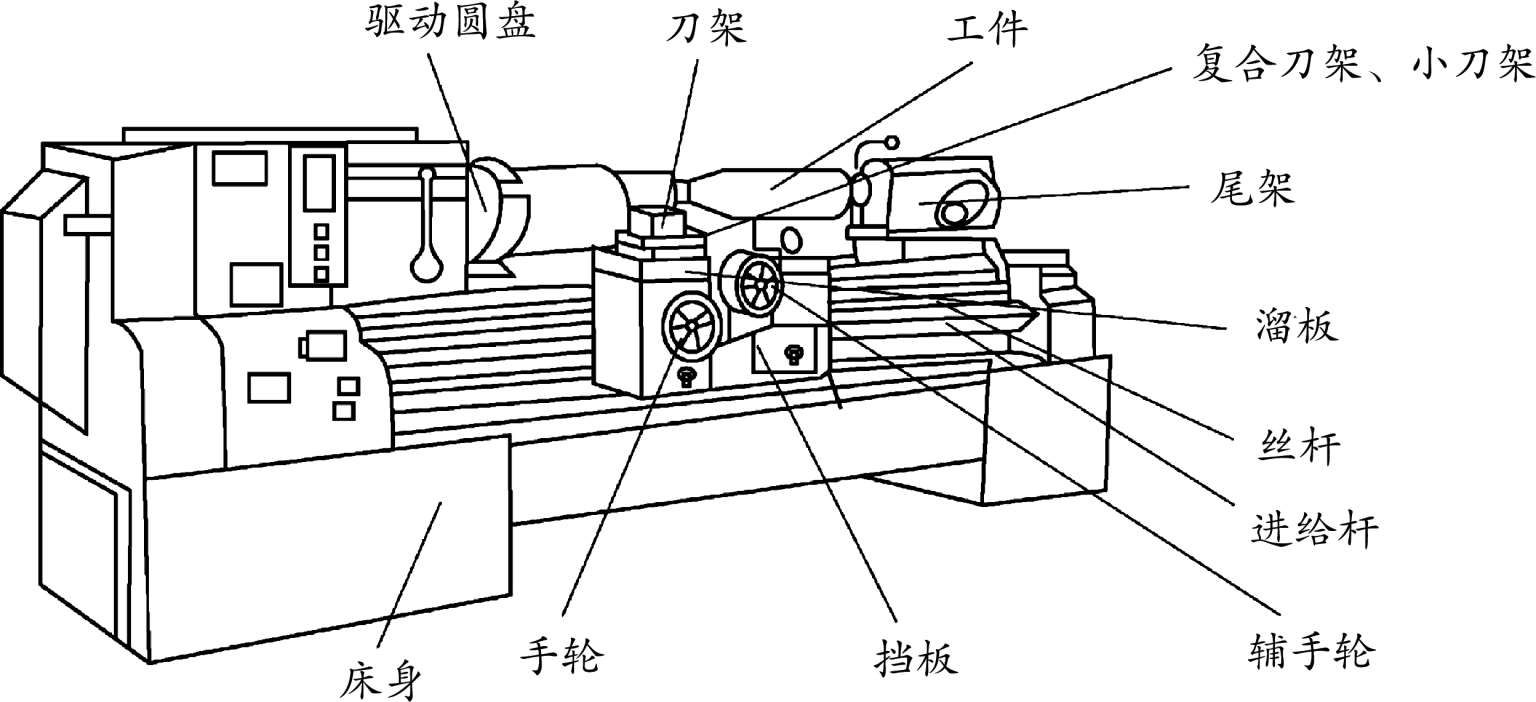
图3-1 普通车床
转塔车床基本上是具有某种附加特性的普通车床,用于半自动加工和减少人工操作误差。转塔车床的拖板设有T型槽,以便在车床导轨两侧安装夹刀装置。这样,当转塔转入合适位置时,可以正确地安装刀具,以便进行切削。拖板装有自动挡铁,以便控制刀具行程,提供良好的重复切削。转塔车床的尾座是六角形结构,可以装六把刀具。虽然操作前刀具和挡铁的安装要花大量时间,但一旦装刀完成,稍微熟练的工人就可以连续重复操作,直到刀具变钝需要更换为止。这样,为加工所做的准备时间相对于所制造的零件的数量是合理的时候,使用转塔车床在经济上才是可行的。
多轴自动车床装有4、5、6或8根主轴,在每根主轴中装一个工件。各主轴可以围绕着一根中心轴来转换位置,而主刀具溜板可以接近所有的主轴。每根轴位上都装有一侧向可以独立操作的刀具滑板。各刀具滑板都是靠凸轮操作的,因此,加工准备可能要花几天时间,至少5 000件的批量生产,它的使用才是合理的。这种机床的主要优点是所有的刀具能同时工作,因而一个工人可以看管几部机床。对于相对简单的零件,多轴自动车床可以在5秒内生产加工出一件产品。
Most of the mechanical operations are commonly performed on five basic machine tools:
(1)The drill press
(2)The lathe
(3)The shaper or planer
(4)The milling machine
(5)The grinder
Drilling is performed with a rotating tool called a drill.Most drilling in metal is done with a twist drill.The machine used for drilling is called a drill press. Operations,such as reaming and tapping,are also classified as drilling.Reaming consists of removing a small amount of metal from a hole already drilled.Tapping is the process of cutting a thread inside a hole so that a cap screw or bolt may be threaded into it.
The lathe is commonly called the father of the entire machine tool family.For turning operations,the lathe uses a single-point cutting tool which removes metal as it travels past the revolving workpiece [1] .Turning operations are required to make many different cylindrical shapes,such as axes,gear blanks,pulleys,and threaded shafts.Boring operations are performed to enlarge,finish,and accurately locate holes.
Milling removes metal with a revolving,multiple cutting edge tool called milling cutter.Milling cutters are made in many styles and sizes.Some have as few as two cutting edges and others have 30 or more.Milling can produce flat or angled surfaces,grooves,slots,gear teeth,and other profile,depending on the shape of the cutters being used.
Shaping and planing produce flat surfaces with a single-point cutting tool.In shaping,the cutting tool on a shaper reciprocates or moves back and forth while the work is fed automatically towards the tool.In planing,the workpiece is attached to a worktable that reciprocates past the cutting tool.The cutting tool is automatically fed into the workpiece a small amount on each stroke.
Grinding makes use of abrasive particles to do the cutting.Grinding operations may be classified as precision or imprecision,depending on the purpose.Precision grinding is concerned with grinding to close tolerances and very smooth finish[ 2 ].Imprecison grinding involves the removal of metal where accuracy is not important.


[1]For turning operations,the lathe uses a single-point cutting tool which removes metal as it travels past the revolving workpiece.
在车削加工中,车床利用单刃切削刀具对旋转的工件进行金属切除。[句中which引导的是一个定语从句,该从句修饰cutting tool;as引导的是时间状语从句,表示主句的动作(removes metal)与从句的动作(travels past)同时完成,it指刀具]
[2]Precision grinding is concerned with grinding to close tolerances and very smooth finish.
精磨是为了缩小工件公差范围,以及降低表面粗糙度。
大多数机械加工操作通常是在以下五种基本机床上完成的:
(1)钻床
(2)车床
(3)牛头刨床和龙门刨床
(4)铣床
(5)磨床
钻削是由旋转的钻头完成的。大多数金属的钻削由麻花钻来完成。用来进行钻削加工的机床称为钻床。扩孔和攻螺纹也归为钻削,扩孔是从已经钻好的孔上再切除少量的金属。攻螺纹是在内孔上加工出螺纹以使螺杆和螺栓拧进孔内。
车床通常被称为所有类型机床的始祖。在车削加工中,车床利用单刃切削刀具对旋转的工件进行金属切除。用车削可以加工各种圆柱体形状的工件,如轴、齿轮坯、带轮和丝杆轴。镗削可以将孔扩大,加工孔和精准定位孔。
铣削由旋转的、多切削刃的铣刀来完成。铣刀有多种类型和尺寸。有些铣刀只有两个切削刃,而有些则有多达三十或更多的切削刃。铣刀根据使用的刀具不同形状能形成平面、斜面、沟槽、狭槽、齿轮轮齿和其他外形轮廓。
牛头刨床和龙门刨床用单刃刀具来加工平面。用牛头刨床进行加工时,工件朝向刀具自动进给,刀具往复运动。在用龙门刨床进行加工时,工件安装在工作台上,工作台往复经过刀具而切除金属。刀具每完成一个行程则自动向工件进给一个小的进给量。
磨削利用磨粒来完成切削工作。根据加工要求,磨削可分为精密磨削和非精密磨削。精密磨削是为了缩小工件公差范围,以及降低表面粗糙度;在精度要求不高的地方切除多余的金属时,用非精密磨削。