1. To determine the effects of concentration,temperature and catalyst on the rate of a chemical reaction.
2. To determine the rate of the reaction between ammonium persulfate and potassium iodide.
3. To calculate the reaction order and the activation energy.
The reaction of ammonium persulfate and potassium iodide is:

The rate equation for this reaction is:
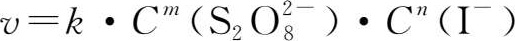
Where v is the reaction rate,and k is the rate constant,
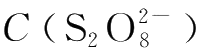 and C(I
-
)are instant concentrations,the sum of m and n is the reaction order.
and C(I
-
)are instant concentrations,the sum of m and n is the reaction order.
The average reaction rate
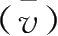 per unit time can be determined by experiments.If the change of concentration for
per unit time can be determined by experiments.If the change of concentration for
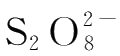 is
is
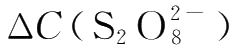 in a period of time(Δt),the average rate can be expressed as:
in a period of time(Δt),the average rate can be expressed as:
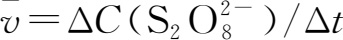
WhenΔt→0,the average rate can be regarded as the approximate instantaneous rate.
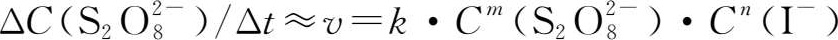
In order to determine the concentration of
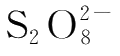 ,a constant known amount of Na
2
S
2
O
3
and starch solution are added when mixing KI with(NH
4
)
2
S
2
O
8
.Then two reactions,(4-1)and(4-2),occur at the same time.
,a constant known amount of Na
2
S
2
O
3
and starch solution are added when mixing KI with(NH
4
)
2
S
2
O
8
.Then two reactions,(4-1)and(4-2),occur at the same time.

Reaction(4-2)is very fast and can be completed instantly,while reaction(4-1)is much slower than reaction(4-2).
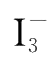 produced by reaction(4-1)reacts with
produced by reaction(4-1)reacts with
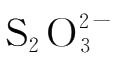 immediately to form colorless
immediately to form colorless
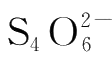 and I
-
.Therefore,in the beginning of the reaction,the unique blue color of
and I
-
.Therefore,in the beginning of the reaction,the unique blue color of
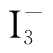 and starch could not be seen.Once Na
2
S
2
O
3
is used up,
and starch could not be seen.Once Na
2
S
2
O
3
is used up,
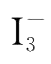 still being formed by reaction(4-1)will react with starch and appear blue.
still being formed by reaction(4-1)will react with starch and appear blue.
From reaction(4-1)and(4-2),we can find that each mole of
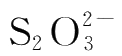 used is equivalent to 1/2 mole of
used is equivalent to 1/2 mole of
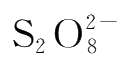 used.
used.
In this experiment,the initial concentration of Na
2
S
2
O
3
is the same for each mixture.Since the blue solution indicates that
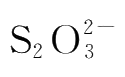 is used up,the initial concentration of Na
2
S
2
O
3
can be used to calculateΔC
is used up,the initial concentration of Na
2
S
2
O
3
can be used to calculateΔC
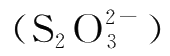 and the average reaction rate.
and the average reaction rate.
In logarithmic form,the rate equation becomes:
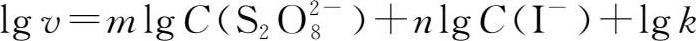
When C(I
-
)is kept constant,a plot of
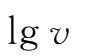 versus
versus
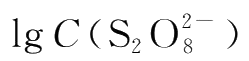 produces a straight line with a slope equal to m.In the same way,a plot of
produces a straight line with a slope equal to m.In the same way,a plot of
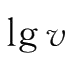 versus
versus
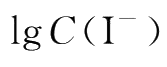 produces a straight line with a slope equal to n when
produces a straight line with a slope equal to n when
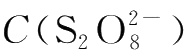 is kept constant.
is kept constant.
Then the value of k,the reaction rate constant,can be calculated with the already known m,n,
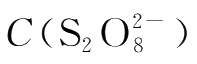 ,C(I
-
)and v.
,C(I
-
)and v.
According to the Arrhenius equation,
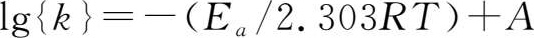
where k is rate constant,kJ·mol -1 ;E a is activation energy(kJ·mol -1 );R is gas constant(R=8.314 J·K -1 ·mol -1 );T is thermodynamic temperature;A is constant.
Determine the different k values at different temperatures.A plot of
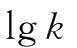 versus 1/T produces a straight line with a slope of
versus 1/T produces a straight line with a slope of
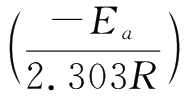 ,so the activation energy can be calculated.
,so the activation energy can be calculated.
Beakers(100mL);large test tube;volumetric cylinder;thermostatic water bath;stopwatch;thermometer.
(NH 4 ) 2 S 2 O 8 (0.2 mol·L -1 );freshly prepared);KI(0.2 mol·L -1 );KNO 3 (0.2 mol·L -1 );Na 2 S 2 O 3 (0.05 mol·L -1 );(NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 (0.2 mol·L -1 );Cu(NO 3 ) 2 (0.02 mol·L -1 );starch solution(2%,wt/wt).
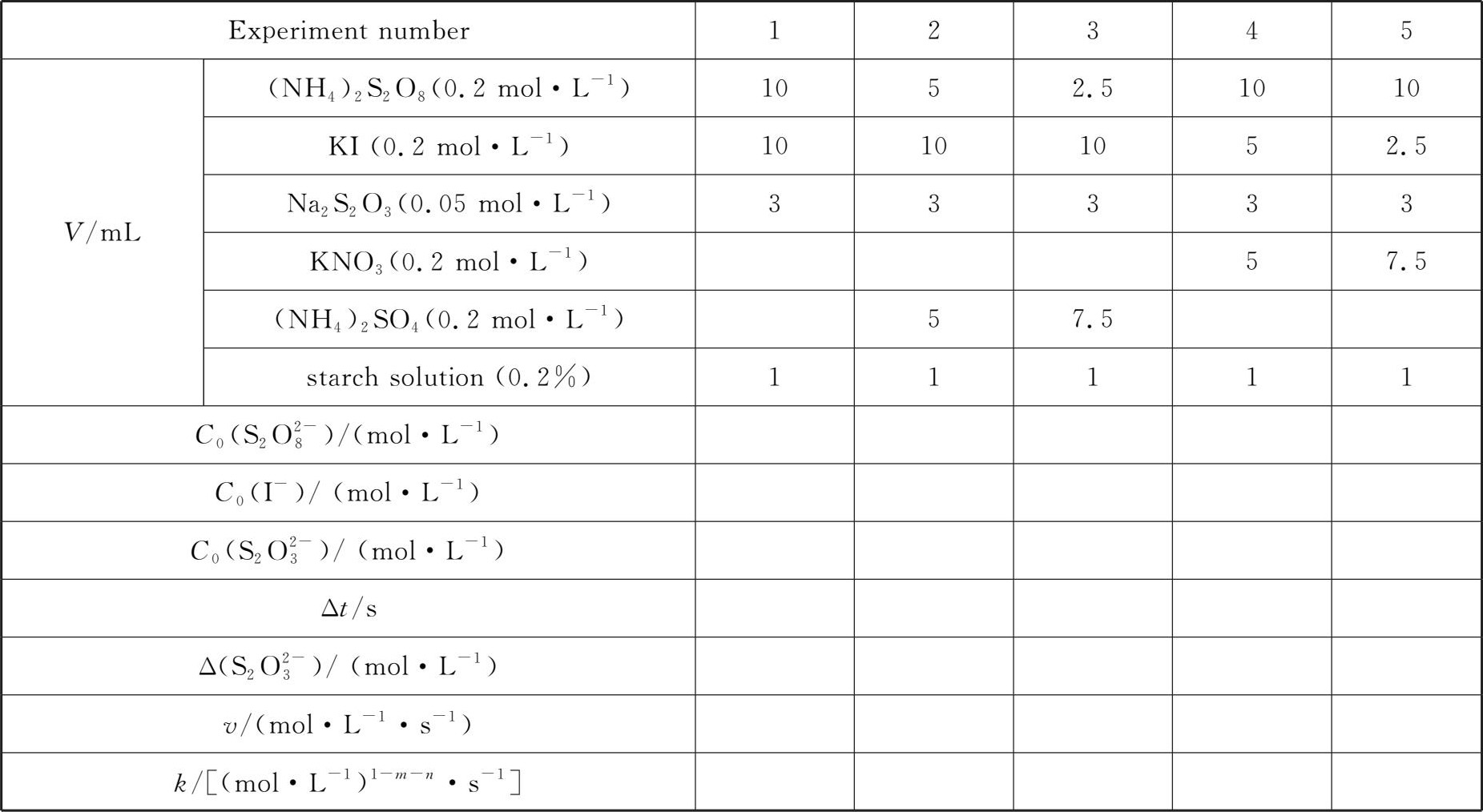
At room temperature,the dosage of reagents listed in table 4-1 shall be accurately measured by the volumetric cylinder.Except for(NH 4 ) 2 S 2 O 8 solution,other reagents can be mixed in the beaker with corresponding number according to the dosage.When(NH 4 ) 2 S 2 O 8 solution is added,the time shall be counted immediately to mix the solution evenly.When the solution turns blue,the time shall be stopped,and the timeΔt and the room temperature shall be recorded.
Table 4-1 Effect of concentration on the reaction rate Room temperature: ___℃
According to the reagent dosage of Experiment 1 in Table 4-1,the experiment was continued at 5℃ ,10℃ and 15℃ higher than the room temperature.Record the measured reaction time,calculate reaction rate and rate constant at each temperature in Table 4-2.
Table 4-2 Effect of temperature on the reaction rate

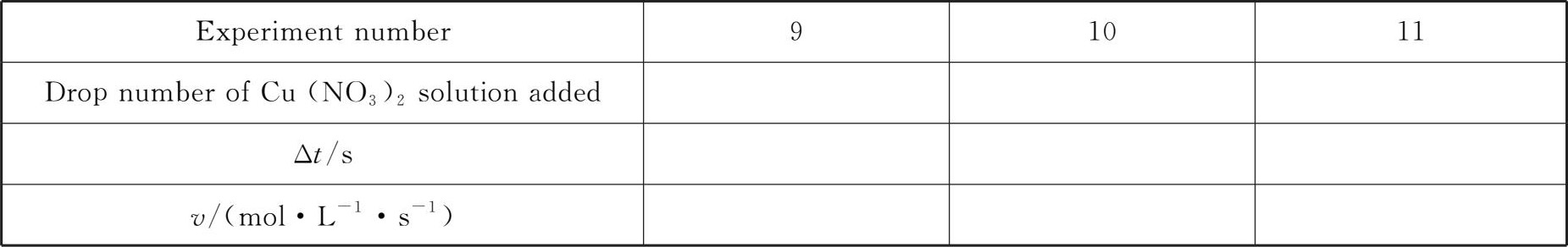
At room temperature,add 1 drop,5drops and 10drops of Cu(NO 3 ) 2 solution respectively according to the reagent dosage of Experiment 1 in Table 4-1.For the experiment with less than 10drops,quickly add (NH 4 ) 2 S 2 O 8 solution to 10 drops,stir,time,and compare the reaction rate of this experiment with that of Experiment 1 in Table 4-1.
Table 4-3 Effect of catalyst on the reaction rate
1. Why can the reaction rate be calculated by the time lapse from the beginning of the reaction till the deep blue color appears in the experiment?Do the reactions continue or cease when the deep blue color appears?
2. How will it affect the results if the amount of Na 2 S 2 O 3 is too much or too little?
continued