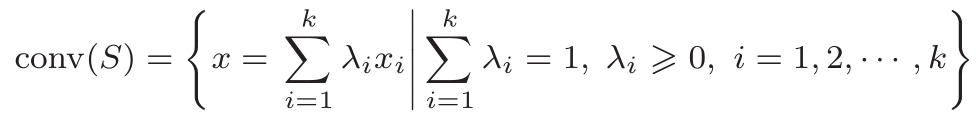 参考文献
参考文献
[1]Rosenblatt F. The Perceptron:a probabilistic model for information storage and organization in the Brain. Cornell Aeronautical Laboratory. Psychological Review, 1958, 65(6):386–408.
[2]Novikoff A B. On convergence proofs on perceptrons. Symposium on the Mathematical Theory of Automata, Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn, 1962, 12, 615–622.
[3]Minsky M L, Papert S A. Perceptrons . Cambridge, MA:MIT Press. 1969.
[4]Gallant SI. Perceptron-based learning algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1990, 1(2):179–191.
[5]Freund Y, Schapire R E. Large margin classification using the perceptron algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference on Computational Learning Theory(COLT’98). ACM Press, 1998.
[6]Li Y Y, Zaragoza H, Herbrich R, et al. The Perceptron algorithm with uneven margins. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Machine Learning. 2002, 379–386.
[7]Widrow B, Lehr M A. 30 years of adaptive neural networks:perceptron, madaline, and backpropagation. Proc. IEEE , 1990, 78(9):1415–1442.
[8]Cristianini N, Shawe-Taylor J. An introduction to support vector machines and other kernel-based learning methods. Cambridge University Press, 2000.
[1] 第7章中会介绍 y ( w · x + b )称为样本点的函数间隔。
[2] 设集合 S ⊂ R n 是由 R n 中的 k 个点所组成的集合,即 S ={ x 1 , x 2 ,…, x k }. 定义 S 的凸壳conv( S )为